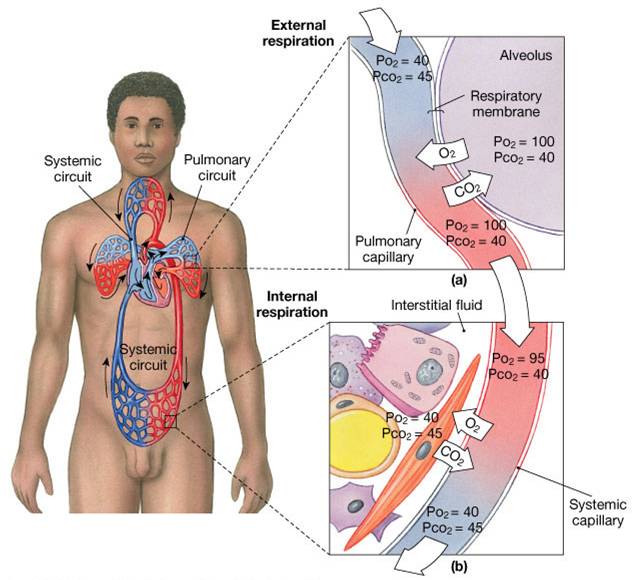
External Respiration Is Best Described as the
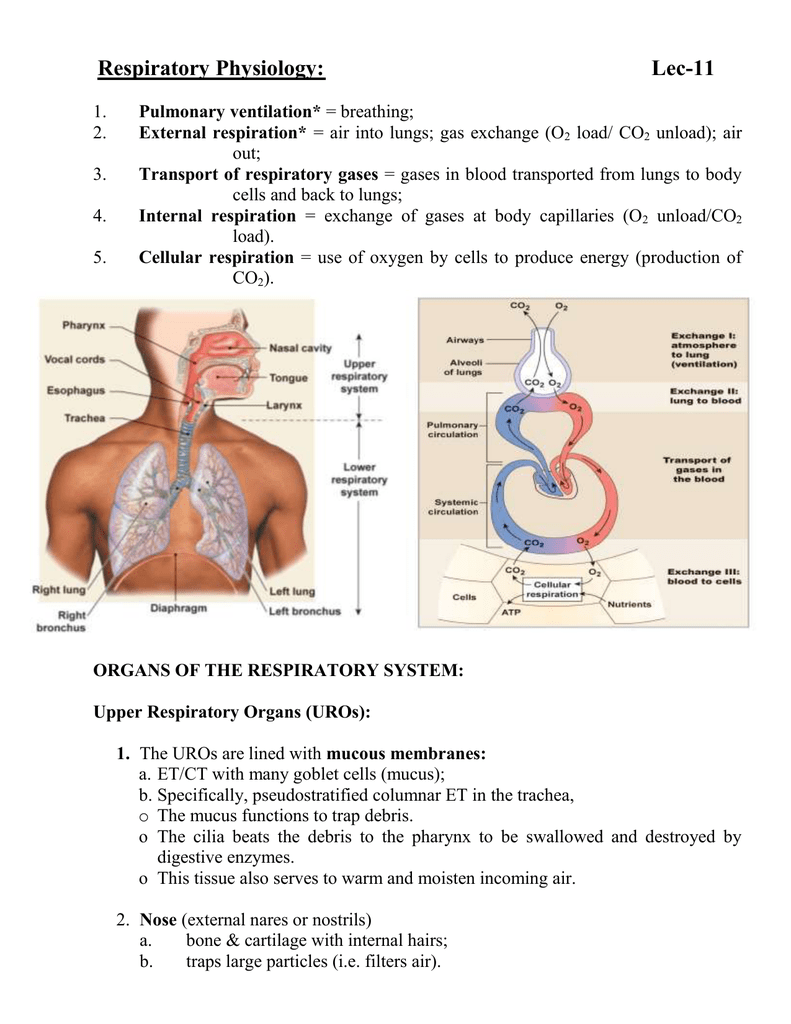
External respiration refers to breathing and exchange of gases between the external environment and lungs and between alveoli surface and the blood stream. O2 transported by hemoglobin internal respiration.
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
It is an exchange of gasses between the blood and the individual cells of the body.

. External respiration is the process of exchanging oxygen carbon dioxide and other blood solutes with the external environment. The process of gas exchange that occurs between the cells and the systemic capillaries is known as. A respiring organism that can utilize different external electron acceptors must a.
Exchange of gases both in and out of the blood occurs simultaneously. The process of moving air from the atmosphere into the alveoli of the lungs as well as back out again. Ventilation and perfusion in the.
The movement of gases between the environment and the bodys cells. It allows easy diffusion of gases between the alveoli and the body. All of the above describe external respiration.
Breathing is the mechanical process of pulling lungs into or out of the lungs or moving water over the gills. Internal respiration refers to gas exchange across the respiratory membrane in the metabolizing tissues. External respiration is best described as the internal respiration.
The exchange of respiratory gases between the alveoli and the pulmonary capillary bed. Which of the following best describes external respiration. Which of the following accurately describes the site of external respiration.
Respiration in whole is the process of delivering oxygen to the cells to extract the energy from sugars in oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. This process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as well as a number of. It is a vital process for life as it supplies oxygen to extract energy from food via internal or cellular respiration.
Up to 25 cash back Which of the following describes external respiration. Breathing Gas exchange The first stage involves ventilation or breathing which is the intake of oxygen into the body and expulsion of carbon dioxide out of the body. What are the processes of external respiration.
Breathing mechanics include breathing rate breathing depth volume of air in a single breath. External respiration is a physical process during which oxygen is taken up by capillaries of lung alveoli and carbon dioxide is released from blood. The actual exchange of gases occurs due to simple diffusion.
-The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the blood. External respiration is a physical process of taking oxygen from the external environment into the body and expelling carbon dioxide from the body to the external environment. The exchange of O2 and CO2 between the air in the alveoli and the blood supplying the alveoli.
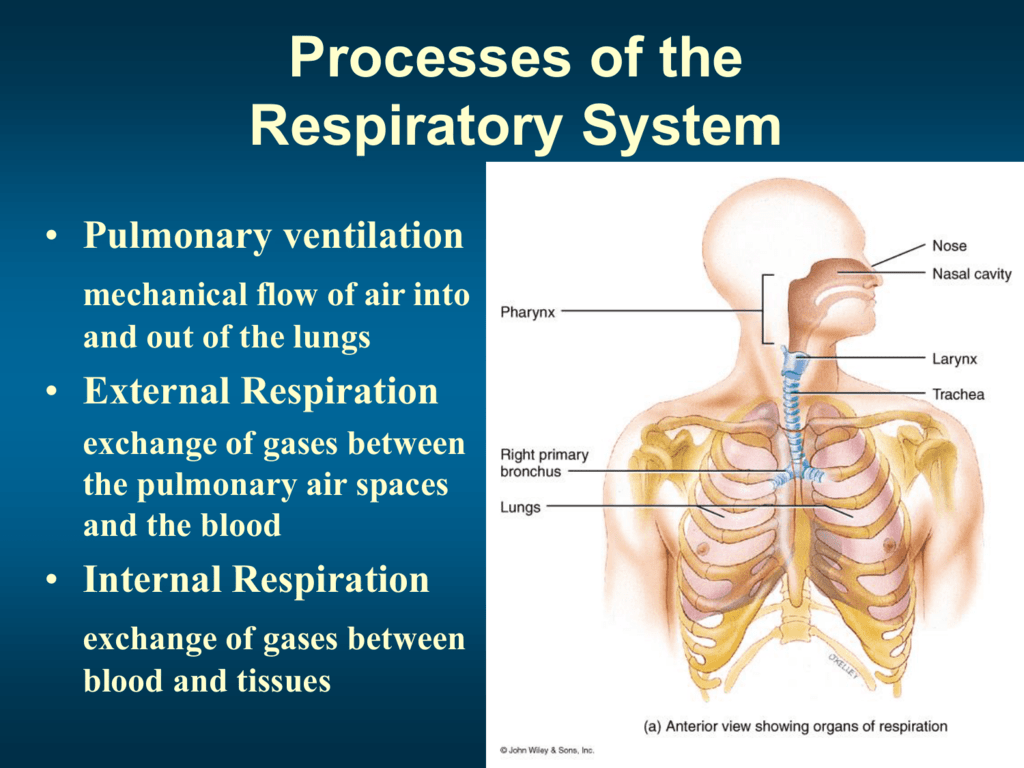
Both A and B. Internal respiration refers to the gaseous exchange between blood and different tissues and cellular respiration process where oxygen is utilised to generate energy in the form of ATPs. It is the trachea bronchi and bronchioles.
Have an NADH Q reductase that can oxidize a variety of substances c. It is an interaction between the diaphragm and the abdominal wall causing the air to move into and out of the lungs. External respiration refers to the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs gills or other tissues exposed to the external environment.
External respiration describes the exchange of gasses between the external environment and the bloodstream. Diffusion of gases across the gas exchange membrane from blood into tissues. -The exchange of air between the atmosphere and the lungs ventilation.
Oxygen diffuses from alveolar air into the blood during external respiration. The diffusion of gases across the gas exchange membrane into blood from the external environment. External respiration is about the mechanics of breathing getting oxygen into the lungs and regulating it in a way that ensures its diffusion into the bloodIt is also about ensuring proper diffusion of CO 2 from the blood into the lungs and its subsequent excretion into the atmosphere.
Oxygen diffuses out from the blood into tissue during internal respiration. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide is higher in the capillaries than the tissue.
You and your partner Mike arrive on scene to find a man standing outside a softball park who has suffered a blunt trauma to the chest. Internal respiration or tissue respirationcellular respiration refers to a metabolic process in which oxygen is released to tissues or living cells and carbon dioxide is absorbed by the blood. It is an exchange of gasses between the air in the lungs and the blood.
It is very thick and covered with a thin layer of mucous. The convective movement of gases via the blood ex. Potentially be able to respire in the presence or absence of O 2 e.
External respiration consists of two stages. CPartial pressure of oxygen is higher D. Medical Definition of external respiration.
In the context of pulmonary ventilation external respiration is best described as. External respiration refers to gas exchange across the respiratory membrane in the lungs. Respiration is the biochemical process in which the cells of an organism obtain energy by combining oxygen and glucose resulting in the release of carbon dioxide water and ATP the currency of.
Partial pressure gradients allow gasses to flow from areas of high pressure to areas of lower pressure. Have terminal reductases that can interact with a variety of external electron acceptors. APartial pressure of oxygen is lower in the capillaries than the tissue.
External respiration also known as breathing refers to a process of inhaling oxygen from the air into the lungs and expelling carbon dioxide from the lungs to the air. External respiration describes respiration that occurs between the external environment and the cells of the body. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases with the internal environment and occurs in the tissues.
Be a strict aerobe d. The components of external respiration include alveolar surface area ventilation and perfusion matching and partial pressure gradients. External respiration refers to the gas exchange across the respiratory membrane of lungs.
Exchange of gases between the external environment and a distributing system of the animal body as the lungs of higher vertebrates or the tracheal tubes of insects or between the alveoli of the lungs.
Processes Of The Respiratory System

Comments
Post a Comment